Welcome to a world beyond our own, where methane rivers flow and cryovolcanoes erupt. A world that has captured the curiosity and fascination of scientists and space enthusiasts alike. A world known as Titan, Saturn’s largest moon.
In this article, we invite you to embark on a journey with us as we explore the wonders of this mysterious moon. From its discovery to its unique features and potential for scientific discovery, we will delve into all that makes Titan a captivating subject of study.
We will discuss the challenges and advancements in exploring Titan, including the groundbreaking Cassini spacecraft mission. We will also compare and contrast Titan’s physical features, composition, and environment with our very own planet Earth.
And lastly, we will explore the impact of Titan on our understanding of the solar system and its potential for future space exploration.
So buckle up and get ready to unveil the secrets of Titan, a journey that will take us to new frontiers and expand our understanding of the universe.
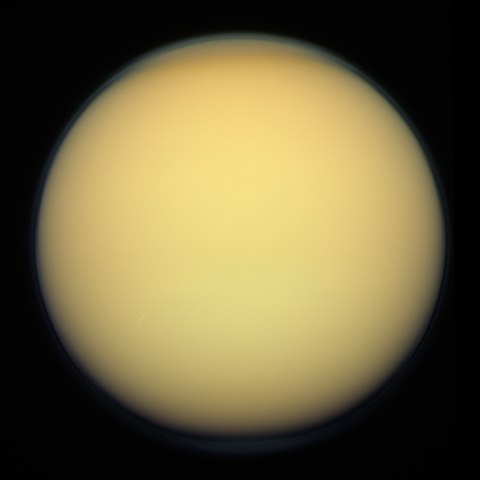

Table of Contents
Titan’s Discovery and Exploration
Titan, the largest moon of Saturn, has long captured the imagination of astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. With its unique features and potential for scientific discovery, Titan has become a focal point in our exploration of the solar system. In this article, we will take you on a journey to unveil the wonders of this fascinating moon.
The discovery of Titan dates back to the 17th century when the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei observed it for the first time through his telescope in 1655. However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that we gained more knowledge about this enigmatic moon. In 1944, Dutch astronomer Gerard Kuiper discovered that Titan has an atmosphere, which sparked further interest in studying this moon.
Exploring Titan has always been a challenging task, mainly due to its extremely distant location from Earth. However, with advancements in technology and space exploration, we have been able to gather more information about this mysterious moon. The most significant breakthrough came in 2004 when the Cassini spacecraft was launched by NASA and ESA on a mission to study Saturn and its moons. This mission provided us with an unparalleled opportunity to explore Titan in detail.
Over the past 13 years, the Cassini mission has provided us with a wealth of information about Titan’s surface and atmosphere. The spacecraft’s radar instrument revealed that Titan has lakes and seas of liquid methane and ethane, making it the only known world other than Earth to have stable bodies of liquid on its surface. The Cassini mission also discovered that Titan has a thick and complex atmosphere, with a composition similar to that of early Earth.
The Cassini spacecraft’s numerous flybys of Titan have allowed us to map and learn about the moon’s diverse surface features. We now know that Titan has a complex geological history, with cryovolcanoes, mountains, and dunes made of organic compounds. The mission also discovered that Titan’s surface is constantly changing due to weather patterns, with methane rain and winds shaping its landscape.
The discoveries made by the Cassini mission have shed light on Titan’s past and potential for habitability. The moon’s atmosphere, composed mainly of nitrogen, methane, and hydrogen, serves as a time capsule that can provide clues about its formation and evolution. Studying Titan’s atmosphere also helps us understand the potential for life on this moon and its potential for human exploration.
While the Cassini mission may have come to an end in 2017, the exploration of Titan is far from over. Future missions like NASA’s Dragonfly, set to launch in 2026, will be the first to land and explore Titan’s surface. This mission will provide us with even more insights into this moon’s geology and potential for life.
In conclusion, the discovery and exploration of Titan have been a remarkable journey, with many more discoveries and advancements yet to come. This moon’s unique features and composition make it a fascinating world to study and continue to expand our understanding of the solar system. Titan’s future in space exploration looks promising, and it may even hold the key to unlocking the mysteries of our universe.
A World of Differences: Titan vs Earth
When we think of a moon, we often picture a barren and desolate landscape, similar to Earth’s own moon. However, Titan, the largest moon of Saturn, couldn’t be more different.
This fascinating moon has captured the imagination of scientists and space enthusiasts alike with its unique and unexpected features.
In this section, we will explore the stark differences between Titan and Earth, shedding light on the mysteries of this enigmatic moon.
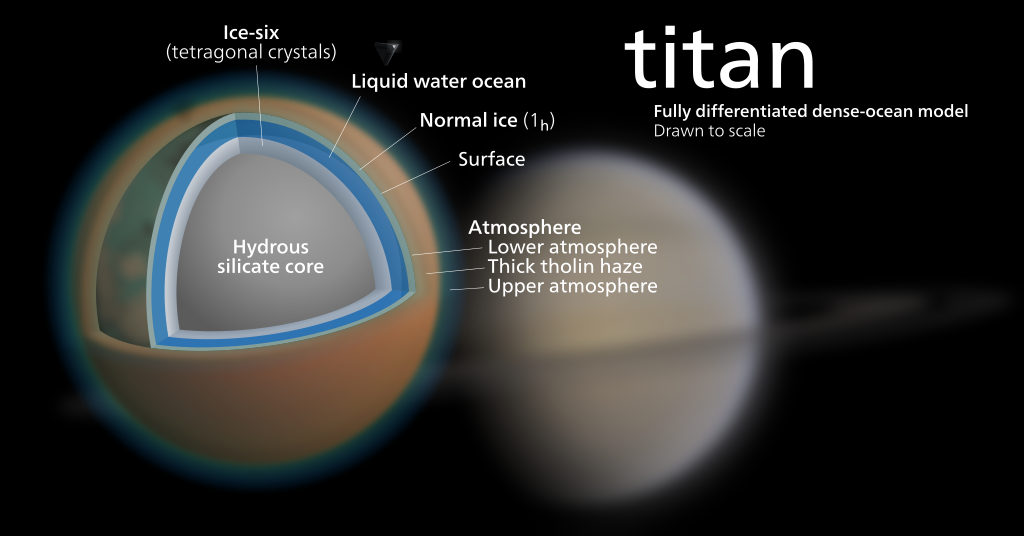
Physical Features and Composition:
The first noticeable difference between Titan and Earth is their size. Titan is the second-largest moon in our solar system, with a diameter of 5,150 kilometers, making it larger than the planet Mercury. In contrast, Earth’s diameter is almost four times that of Titan. This size difference is also reflected in their mass, with Earth being 21 times more massive than Titan.
Another significant difference is the composition of the two bodies. Earth is a rocky planet with a diverse and complex geology, while Titan is a mostly icy world with a rocky core. Titan’s atmosphere is predominantly made up of nitrogen, similar to Earth’s, but it also contains a significant amount of methane, giving it a distinct orange-brown hue. This composition makes Titan the only other body in our solar system, besides Earth, to have a dense atmosphere.
Environment and Conditions:
The environment on Titan is drastically different from that of Earth. With an average surface temperature of -179 degrees Celsius, it is much colder than our planet. The low temperatures, combined with the lack of oxygen, make it impossible for humans to survive on the surface of Titan without protective gear. The surface of Titan is also much younger compared to Earth, with only a few impact craters, suggesting the presence of geological processes that continuously reshape the landscape.
Titan’s environment is also characterized by its abundance of liquid methane and ethane, which play a similar role to water on Earth. These hydrocarbons form lakes, rivers, and even rain on Titan, creating a dynamic and ever-changing environment. However, it’s important to note that the methane on Titan is in a liquid state due to the extremely low temperatures, unlike the gaseous state on Earth.
Impact on Habitability:
The stark differences between Titan and Earth raise the question of whether life could exist on this mysterious moon. While the conditions on Titan are not suitable for life as we know it, the presence of liquid water on its surface could potentially support microbial life. The methane lakes and rivers could also provide a habitat for unique forms of life that have adapted to these extreme conditions.
The differences between Titan and Earth also have implications for future human exploration. Understanding the impact of the environment on human health and technology is crucial for planning successful missions to Titan. Additionally, studying Titan’s unique geology and atmosphere can provide valuable insights into how planets and moons form and evolve, expanding our understanding of the solar system as a whole.
In conclusion, despite being a moon, Titan is a world of its own, with distinct and intriguing features that set it apart from Earth. Its size, composition, and environment make it a fascinating subject for scientific study and a potential destination for future space missions. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of this moon, we are sure to discover even more differences and similarities between Titan and Earth, further expanding our knowledge of the vast universe we live in.
The Mysteries of Titan’s Atmosphere
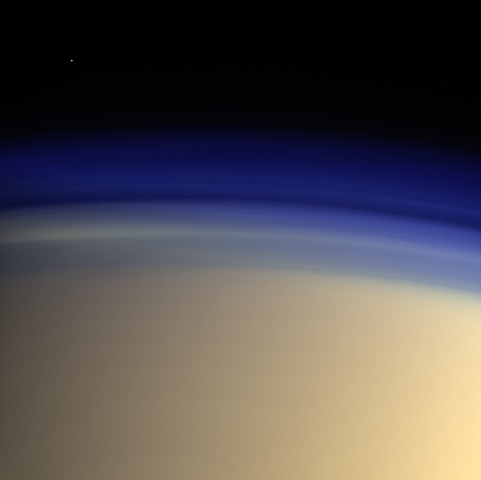
Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, has long captured the imagination of scientists and space enthusiasts alike. With its thick orange haze and intriguing geological features, this enigmatic moon has been a constant source of fascination and wonder. But it’s not just its appearance that makes Titan stand out – its atmosphere holds secrets that could unlock the mysteries of our solar system.
Titan’s atmosphere is composed primarily of nitrogen, making it similar to Earth’s atmosphere. However, it also contains significant amounts of methane, ethane, and other hydrocarbons, giving it a unique and complex chemistry. This composition is a result of Titan’s dense atmosphere trapping gases and preventing them from escaping into space.
But what makes Titan’s atmosphere truly fascinating are its weather patterns. Despite its freezing temperatures of around -290°F, Titan experiences a hydrological cycle similar to that of Earth. Rain, clouds, and even a form of liquid methane called “methane lakes” can be found on this moon. These features have led scientists to hypothesize that there may be a liquid water ocean beneath Titan’s surface, making it a potential host for life.
Studying Titan’s atmosphere has been a challenge due to its thick haze, which has obscured much of its surface from view. However, the Cassini mission, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017, provided valuable insights into this mysterious moon. It revealed that Titan’s atmosphere is constantly changing, with strong winds and seasonal weather patterns. The spacecraft also discovered that Titan’s atmosphere is rich in organic molecules, making it an ideal environment for studying the chemical processes that could have led to the formation of life.
The ongoing research and analysis of data from the Cassini mission have shed light on the significance of Titan’s atmosphere. It not only provides clues about the moon’s past but also holds the key to understanding its potential for habitability. Studying Titan’s atmosphere can also give us valuable insights into the formation and evolution of other planets and moons in our solar system.
NASA’s upcoming Dragonfly mission, scheduled to launch in 2026, will further explore Titan’s atmosphere and surface. This rotorcraft will land on multiple locations on Titan and study its geological features and potential for life. It will also collect samples of Titan’s atmosphere to analyze back on Earth, providing a deeper understanding of this mysterious moon.
In conclusion, Titan’s atmosphere is a complex and ever-changing environment that holds the key to unlocking many mysteries of our solar system. Its unique composition and weather patterns make it a valuable target for further research and exploration. With ongoing and future missions, we may soon uncover even more about this fascinating moon and its role in shaping our understanding of the universe.
Titan’s Fascinating Geology
Titan’s geological features are as diverse as they are fascinating. From methane lakes to rivers and cryovolcanoes, this moon of Saturn has captured the curiosity of scientists and space enthusiasts alike. In this section, we will dive into the geological wonders of Titan and discuss their significance in shaping the moon’s past and potential for habitability.
The most striking feature of Titan’s geology is its vast methane lakes, which cover almost 2% of its surface. These lakes are formed by the condensation of methane in Titan’s cold and dense atmosphere. The largest and most prominent of these lakes is Kraken Mare, which is around the size of the Caspian Sea on Earth. These lakes not only provide a unique landscape for Titan but also raise questions about the possibility of life in these methane-rich environments.
In addition to lakes, Titan is also home to winding rivers that cut through its surface. These rivers are not made of water like on Earth but are instead composed of liquid methane. This makes them the only known rivers beyond our planet’s boundaries. The discovery of these rivers has led scientists to believe that Titan experiences a cycle similar to Earth’s water cycle, but with methane as the key component.

One of the most intriguing geological features on Titan is its cryovolcanoes. These are volcanoes that erupt not with molten rock but with a slushy mix of water and ammonia. These cryovolcanoes are thought to be the result of a mix of Titan’s interior heat and the presence of liquid water beneath the moon’s icy crust. Some of these cryovolcanoes have been found to reach heights of up to 1,500 meters, making them the tallest known volcanic structures in the solar system.
The geological processes on Titan play a significant role in shaping the moon’s surface and potential for life. The presence of liquid methane and cryovolcanoes suggests that there could be a subsurface ocean of liquid water, creating the perfect conditions for life to thrive. This has led to numerous research studies and theories about the possibility of microbial life on Titan.
To further study and explore Titan’s geology, NASA’s Dragonfly mission is set to launch in 2027. This mission will send a rotorcraft to the moon’s surface, allowing for a closer look at its geological features and potential for habitability. The data and samples collected by Dragonfly will provide valuable insights into the geological processes at work on Titan and the potential for life on this intriguing moon.
The geological features of Titan are not only fascinating on their own but also provide valuable insights into the evolution and composition of our solar system. Studying Titan’s geology can help us understand the formation and processes of other moons and planets in our solar system, such as Pluto and Neptune’s moon Triton. This knowledge is crucial in expanding our understanding of the universe and our place within it.
In conclusion, Titan’s geology is a complex and diverse subject that continues to intrigue and challenge scientists. Its methane lakes, rivers, and cryovolcanoes offer a unique landscape for exploration and provide valuable insights into the past and potential of this mysterious moon. With future missions planned to further study and explore Titan’s geological wonders, we can only imagine what other surprises this fascinating moon has in store for us.
Titan’s Impact on Our Understanding of the Solar System
Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, has captivated scientists and space enthusiasts alike since its discovery in 1655 by Galileo. As we continue to explore this fascinating moon, it has become increasingly clear that Titan holds the key to unlocking many mysteries of our solar system.
With its unique features and composition, Titan has the potential to greatly impact our understanding of the universe. In this section, we will delve into the significance of Titan’s discoveries and how they have expanded our knowledge of the solar system.
One of the most significant impacts of studying Titan is its role in expanding our understanding of the building blocks of our solar system. Titan’s thick atmosphere, composed primarily of nitrogen and methane, is similar to that of early Earth. This has led scientists to hypothesize that Titan may hold clues to the conditions on our planet during its early stages of development. By studying Titan’s atmosphere, we can gain insights into the formation and evolution of Earth’s atmosphere and the potential for life on other planets.
In addition to its atmosphere, Titan’s surface features have also provided valuable information about the geology of our solar system. The discovery of methane lakes, rivers, and cryovolcanoes on Titan has challenged our understanding of how these geological processes work.
Through studying these features, we can gain a better understanding of how similar processes may occur on other moons and planets in our solar system. This has opened up new avenues for research and exploration as we seek to understand the diversity of our universe.
Moreover, Titan’s unique composition and environment have also sparked interest in the search for extraterrestrial life. The presence of liquid on its surface, along with its thick atmosphere and organic compounds, have led scientists to consider the possibility of life on Titan. Recent studies have shown that Titan’s methane-based chemistry may be capable of sustaining microbial life. This has sparked further research and theories on the potential habitability of Titan and other similar environments in our solar system.
Furthermore, Titan’s intriguing features have also played a crucial role in shaping future space missions. The success of the Cassini spacecraft mission, which explored Titan for over 13 years, has inspired scientists to plan further missions to this enigmatic moon.
In fact, NASA’s Dragonfly mission, set to launch in 2026, will send a drone-like spacecraft to explore Titan’s surface and search for evidence of past or present life. This mission has the potential to greatly expand our knowledge of Titan and its impact on our understanding of the solar system.
In conclusion, Titan’s unique features and composition have greatly expanded our understanding of the solar system. From its thick atmosphere to its diverse geological features, Titan continues to fascinate and challenge our understanding of the universe.
With ongoing research and future missions planned, it is clear that this moon will continue to play a crucial role in our exploration and understanding of the solar system. As we continue to unveil the mysteries of Titan, we are sure to uncover even more wonders and mysteries of our vast and ever-evolving universe.
Other links
Some other content you may find interesting
